Stegosaurus is a genus of stegosaurid thyreophoran dinosaurs. They lived at the end of the Jurassic period, approximately 156 and 144 million years ago, in the Kimmeridgian and Titonian, in what is now North America.
Now, you can find these amazing creatures here. There are stegosaurus coloring pages you can get for free. Please choose your favorite and color them.
Free Stegosaurus Coloring Pages

baby stegosaurus coloring page 
coloring pages of stegosaurus 
printable coloring pages of stegosaurus 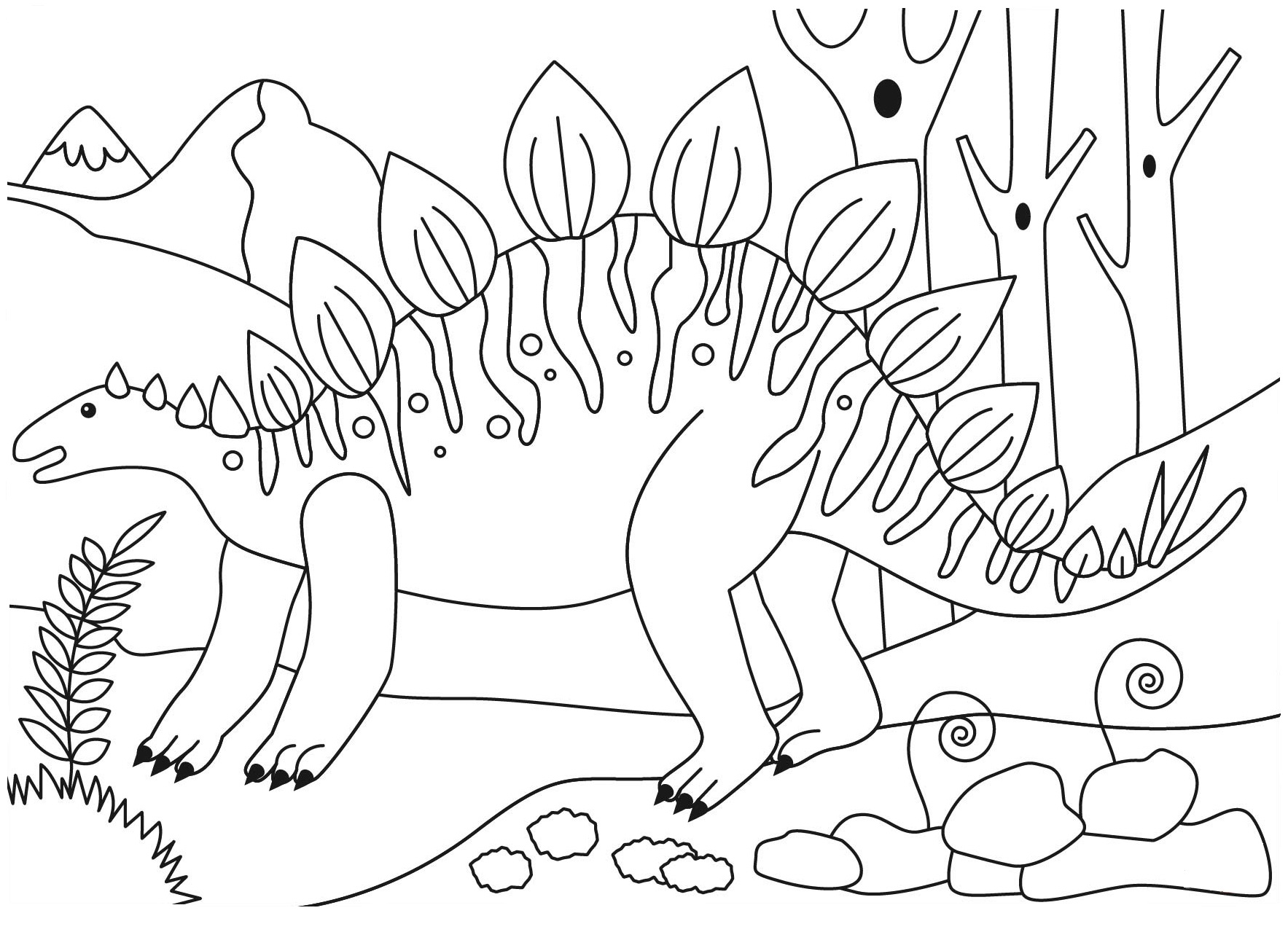
stegosaurus color page 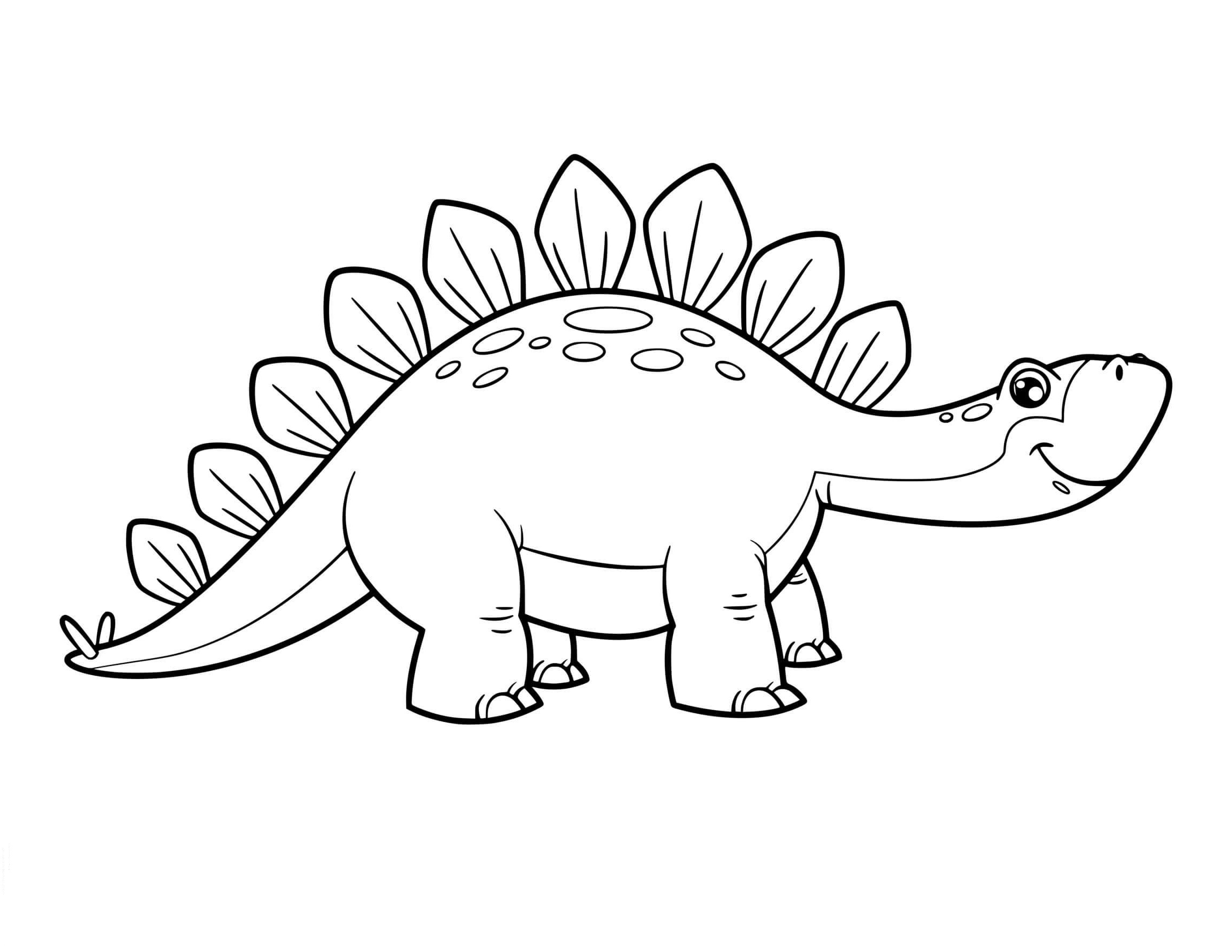
stegosaurus color pages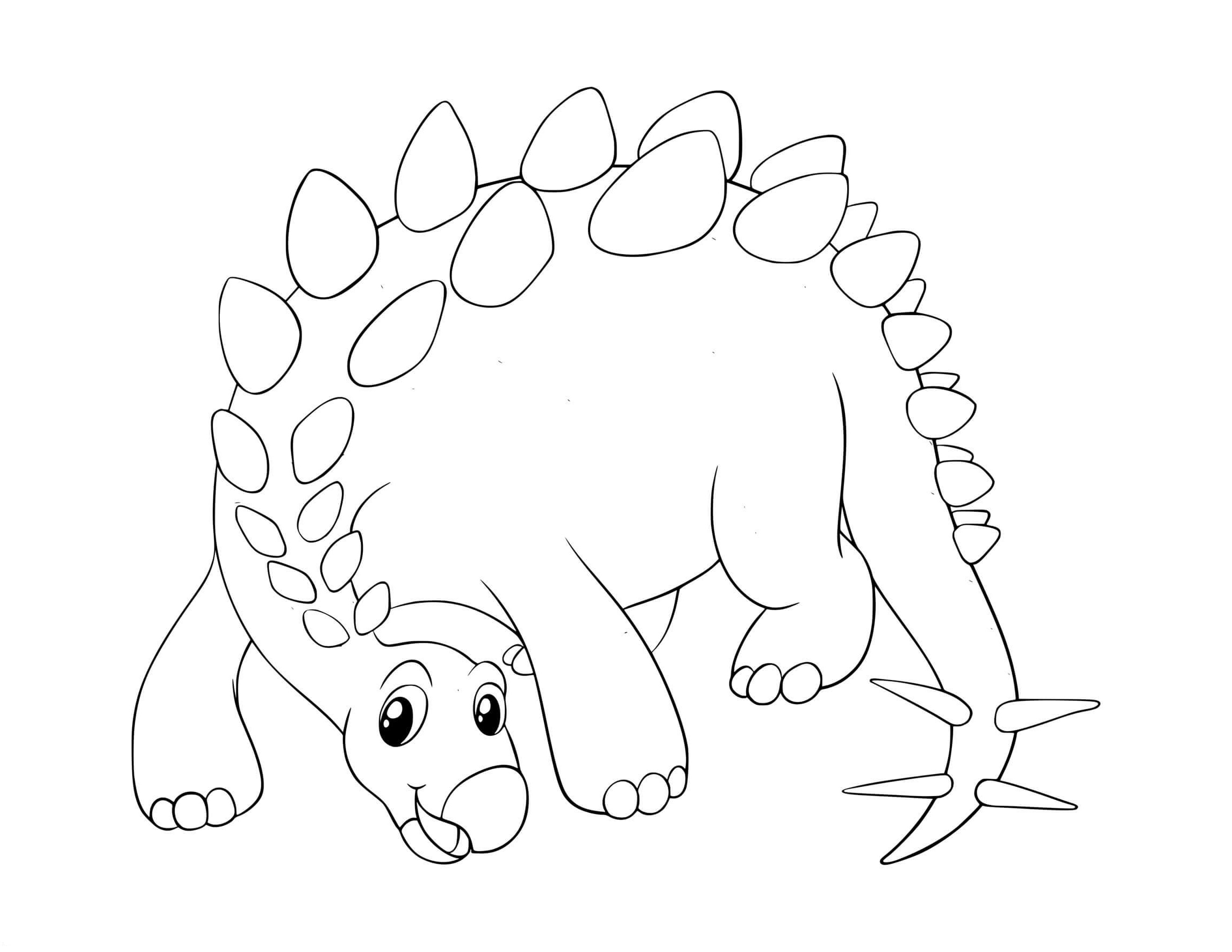 
stegosaurus coloring page 
stegosaurus coloring pages printable 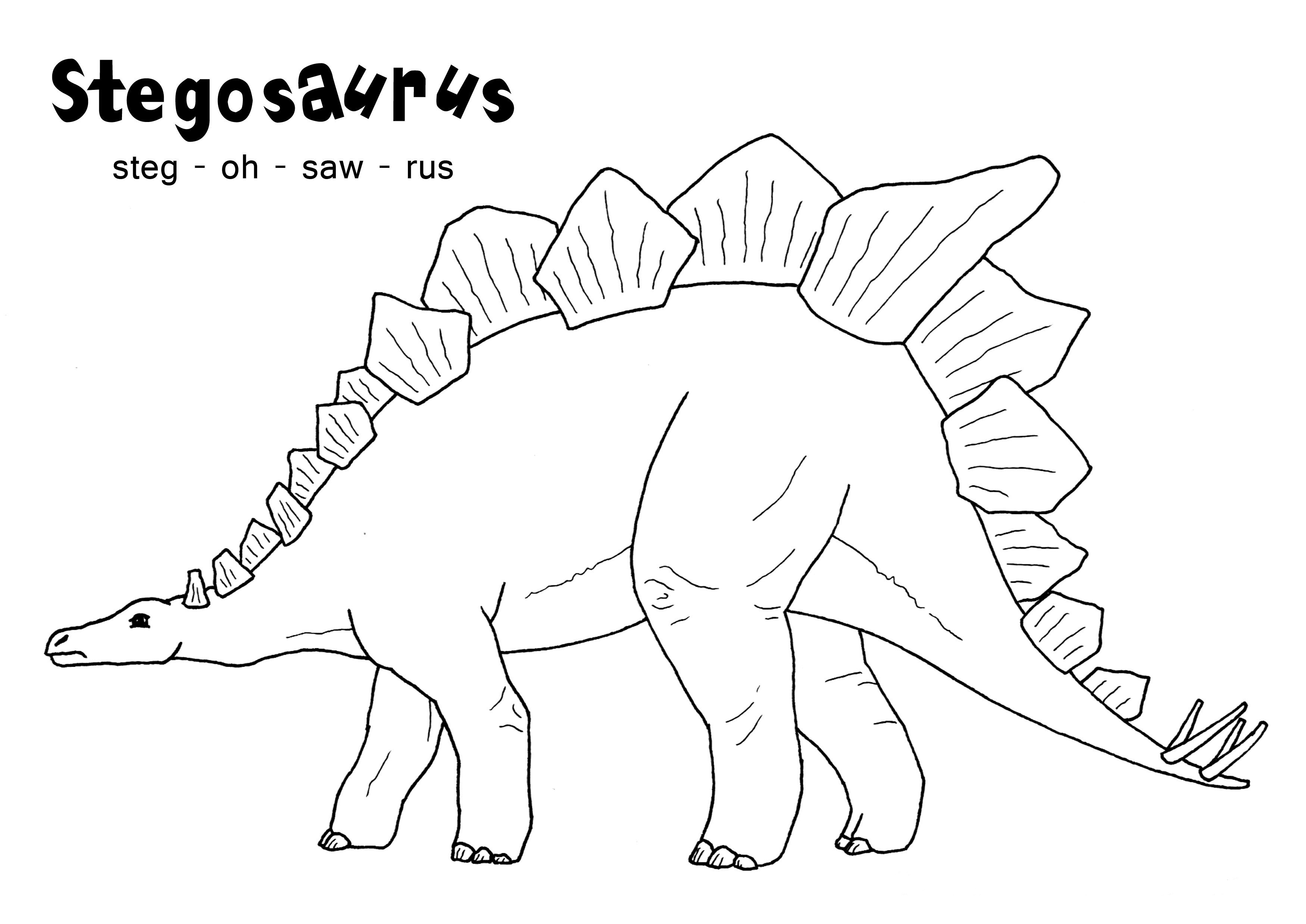
stegosaurus coloring pages 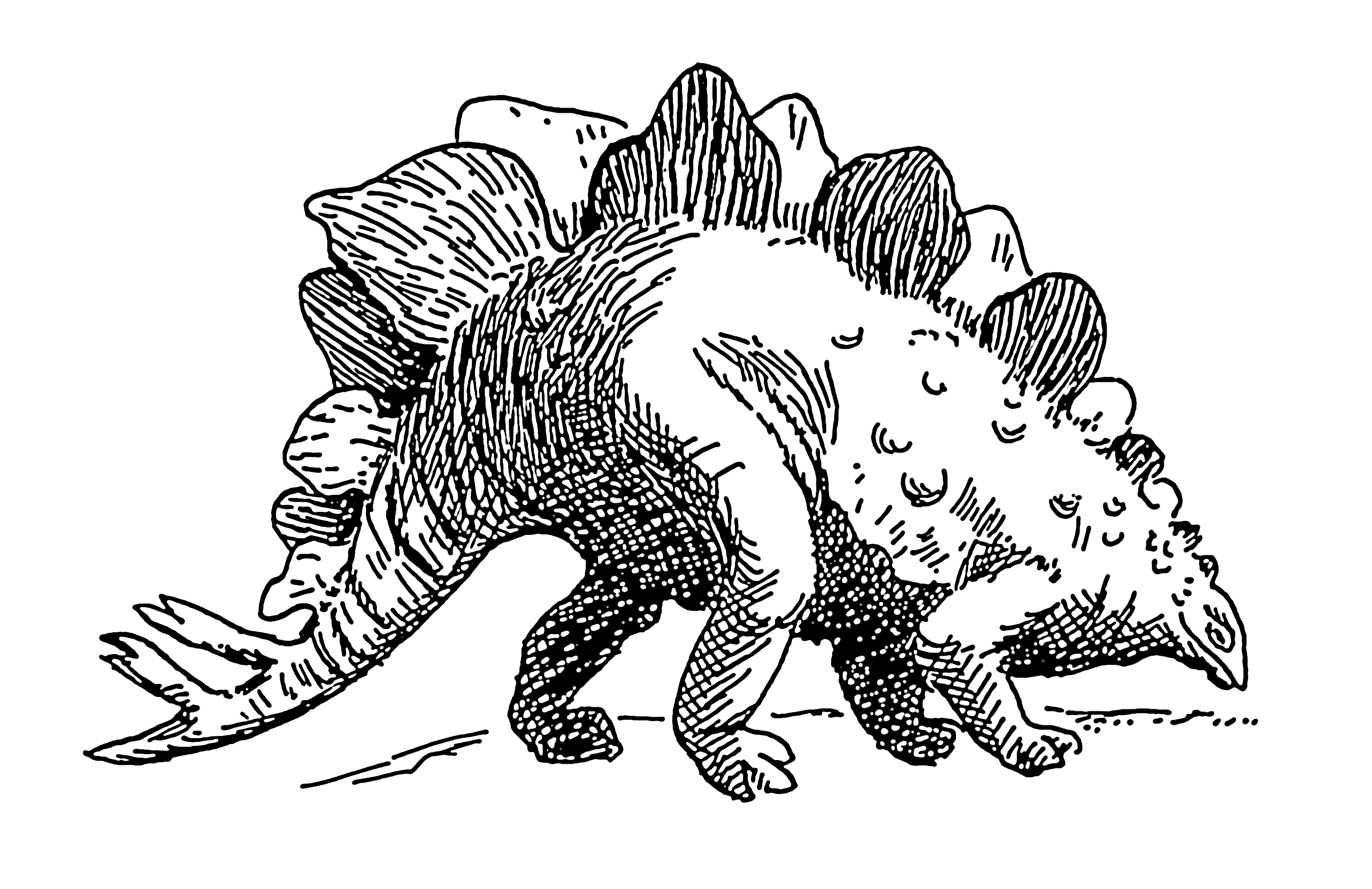
stegosaurus coloring pages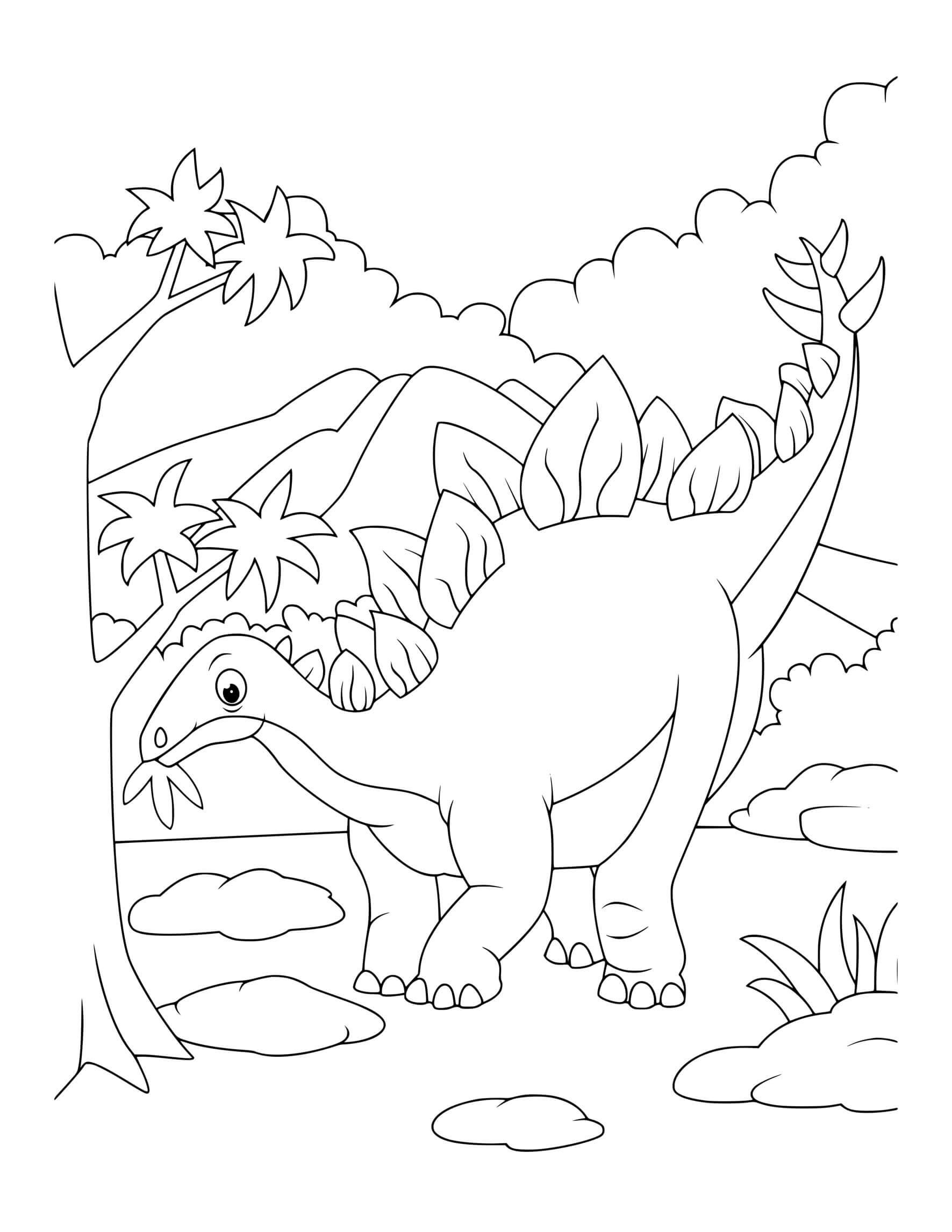 
stegosaurus coloring picture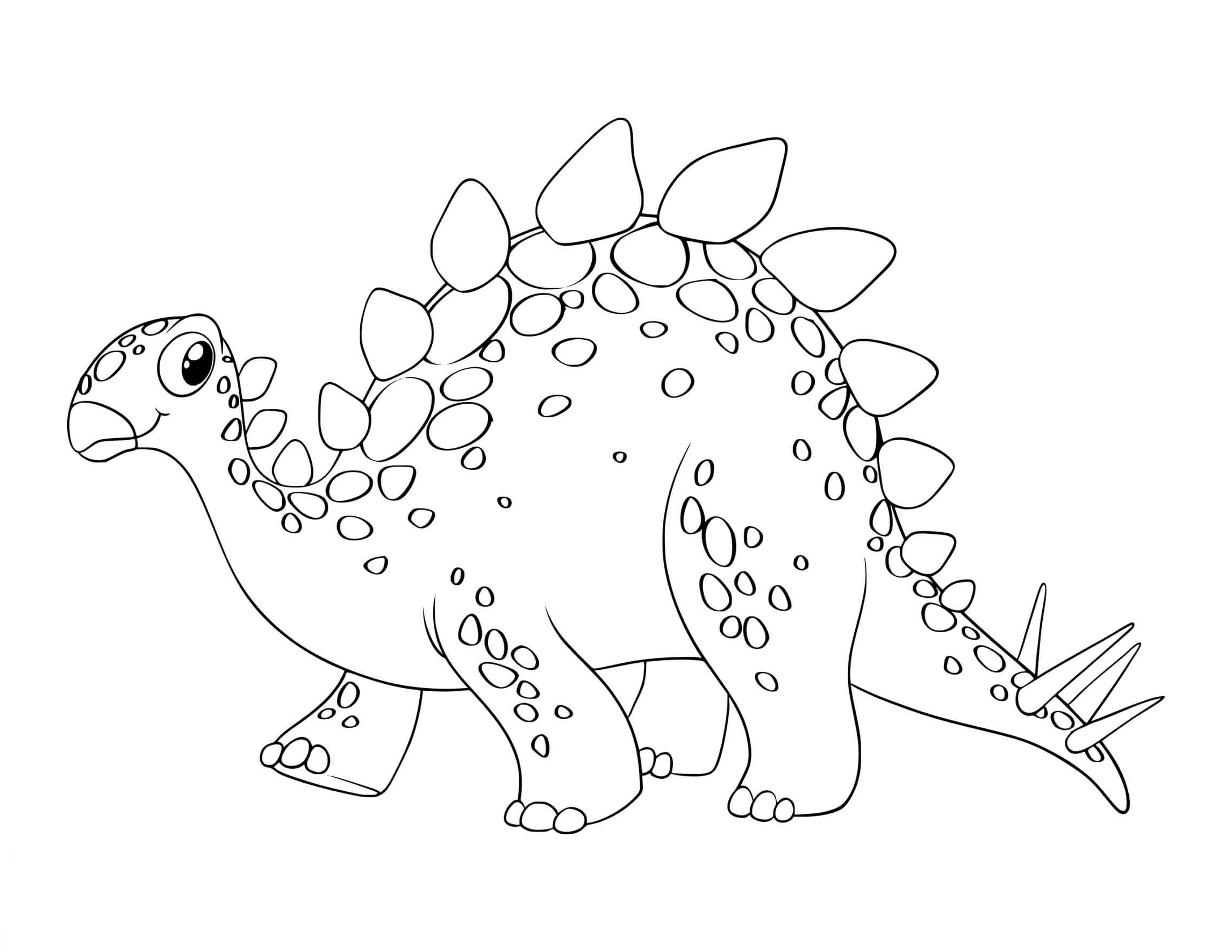 
stegosaurus coloring sheet 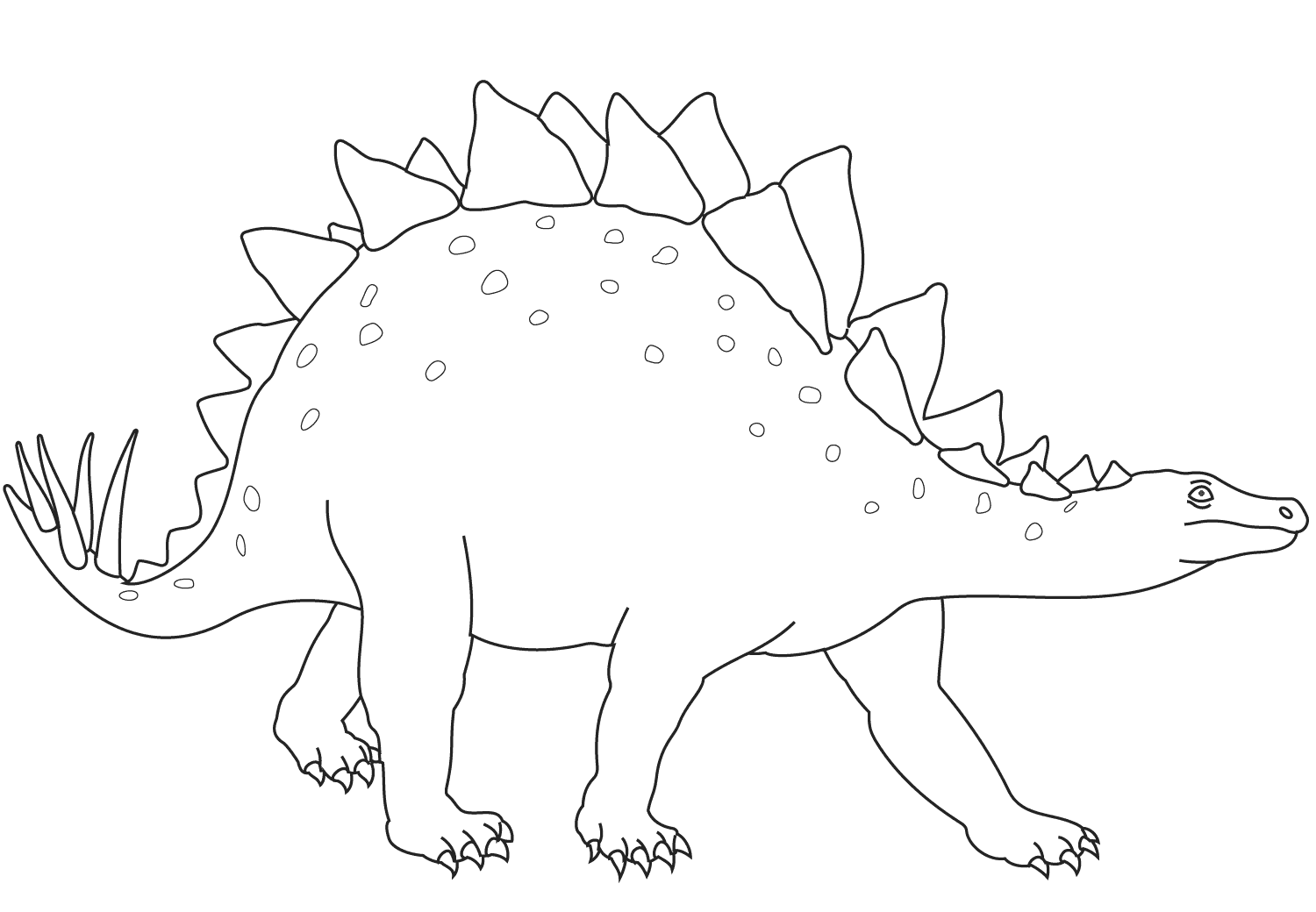
stegosaurus colouring in page 
stegosaurus dinosaur coloring pages 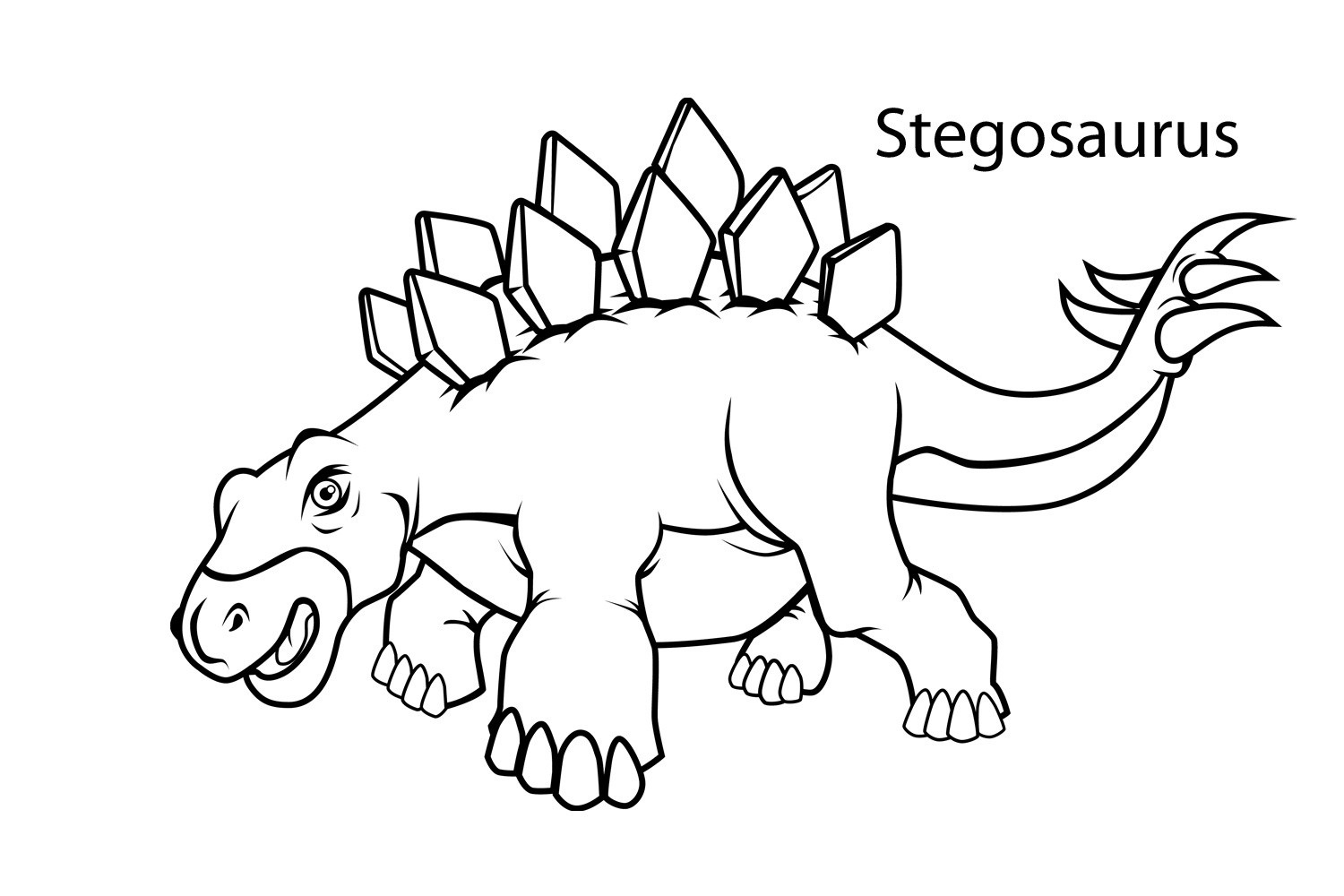
stegosaurus rex coloring page
A large, heavily built, quadrupedal herbivore, Stegosaurus had a distinctive and unusual posture, with a strongly arched back, short forelimbs, head close to the ground, and stiff tail held high in the air. Its arsenal of plates and spikes has been the subject of much conjecture.
The spines were most likely used for defense, while the plates have also been proposed as a defensive mechanism and as part of a display and thermoregulatory functions.
Stegosaurus was one of the largest stegosaurians (larger than Kentrosaurus and Huayangosaurus). Although about the size of a bus shared many anatomical features (including spines and hind plates) with the other stegosaurian genera.
The quadruped Stegosaurus is one of the most easily identifiable dinosaurs due to the distinctive double row of rhomboid plates that rise vertically along its arched back and the two pairs of long spines that extend horizontally near the end of the tail.
The average size of the Stegosaurus is about 9 meters long and 4 meters tall. Although it was a large animal, it was dwarfed by its giant sauropod contemporaries such as Diplodocus, Camarasaurus, and Apatosaurus.
Some form of armor seems necessary, as it coexisted with enormous hunting theropod dinosaurs such as the fearsome Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus.
The hind legs had three short toes, while each foreleg had five toes; only the inner two toes were hoof-shaped. The phalangeal formula is 2-2-2-2-2-1, meaning that the innermost toe of the forelimb has two bones, the next has two, etc.
All four limbs rested on pads behind the toes. The forelimbs were much shorter than the stubby hind limbs, which gave it an unusual posture.
The tail seems to have been held well off the ground, while the head was positioned close to the ground, probably no more than 1 meter above the ground.
The long, narrow skull was small in proportion to the body. It had a small anteorbital fenestra. The hole between the nose and eye typical to most archosaurs, including modern birds, is absent in present-day crocodilians.
The skull in the low position suggests that Stegosaurus may have been a browser of low-growing vegetation. This interpretation is supported by the absence of front teeth and their replacement by a horny beak or rhamphotheca.
The teeth of Stegosaurus were small and triangular; the flat facets from wear indicate that they ground their food. The insertion position of the jaws suggests that Stegosaurus had cheeks to keep food in its mouth while chewing.